Venous thromboembolism (VTE) blood clots diagnosis is a serious preventable medical condition. VTE or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) happens at any age causing serious illness, disability and in some cases, death. VTE is prevented and treated if discovered early. PE in SCD patients is etiologic factor in patients who develop respiratory symptoms. Xray imaging procedure scans chest for blood clots treated with full-dose anticoagulation. Diagnosis of venous thromboembolism by positive Duplex ultrasound, ventilation-perfusion scan, or computed tomography angiography in most cases. Radiology reports for patients documented history of anticoagulation treatment venous thromboembolism cases. This criterion verifies the high specificity history venous thromboembolism. So thromboembolism data collected on date of diagnosis, recurrence, site of thrombosis, central venous catheter-related status. Additional triggering factors includes oral contraceptives, pregnancy, cancer, hospitalization, surgery recorded. Hospitalization associated clots defined by venous thromboembolism occurring 24 hours after admission or within 90-days after discharge. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition of blood clot forming as thrómbōsis. Clots inside blood vessels obstructs flow of blood in circulatory system. If blood vessel vein or artery injured body platelets thrombocytes and fibrin form blood clot to prevent blood loss. Blood vessel if not injured, forms blood clots in body conditions. Pneumococcal sepsis bacteria infection can shut down organs and cause blood clots to block vessels. Cuts off oxygen to cause parts of body to die like kidneys begins to fail. Resuscitated three times, put on ventilating machine help or put in induced coma for further treatment.
Blood clots or pieces of clots break free travel around body embolus block small blood vessels. Symptoms are chest pains shortness of breath, leg pains, problems speaking, or moving parts of body. This clotting factors and platelets used up if bleeding occurs in blood in urine, blood in stool, bleeding in skin. Complications of organ failure if red blood cells cannot deliver oxygen (O2) to body tissues via blood flow circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in lung into the tissues squeezing through body’s capillaries. Blood clot blocks circulation by causing severe pain or bruising mark on the leg. Treatment for pulmonary embolism at a hospital treats underlying causes deep vein thrombosis. Starts anticoagulant medications heparin and warfarin to stop blood clots returning. Pulmonary embolism occurs as clumps of blood clot gets wedged into artery in lungs. Blood clots from leg condition deep vein thrombosis (DVT). A catheter is inserted into vein in the groin upper thigh or arm and threaded to clots in the lung. The doctor may use catheter to remove clot or deliver medicine to dissolve it. Rarely, surgery is needed to remove the blood clot. Clots block oxygen flow 2.4 million erythrocytes produced per second in human adults affected. Blocks red cells developing in bone marrow circulating 100–120 days in the body before component recycled by macrophages. Circulation takes 60 seconds or one minute and a quarter of the cells in human body are red blood cells. And the blood volume is 40% to 45% is red blood cells. Blood related conditions are critical life situations so must be taken urgently, extremely seriously. Every second counts and they must have continous oxygen supply during crises. The blood clots can appear incredibly quickly, due to a number of factors like change in temperature. It causes a number of problems in the body and causes issues heart attacks. If found during routine check ups clot dealt with before obstructing oxygen in red blood portal veins or arteries.
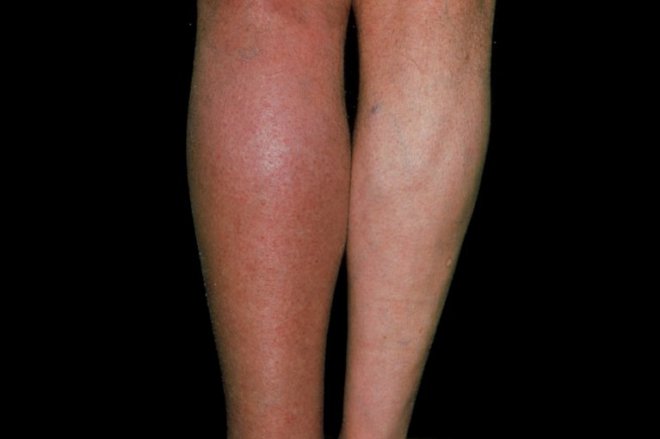
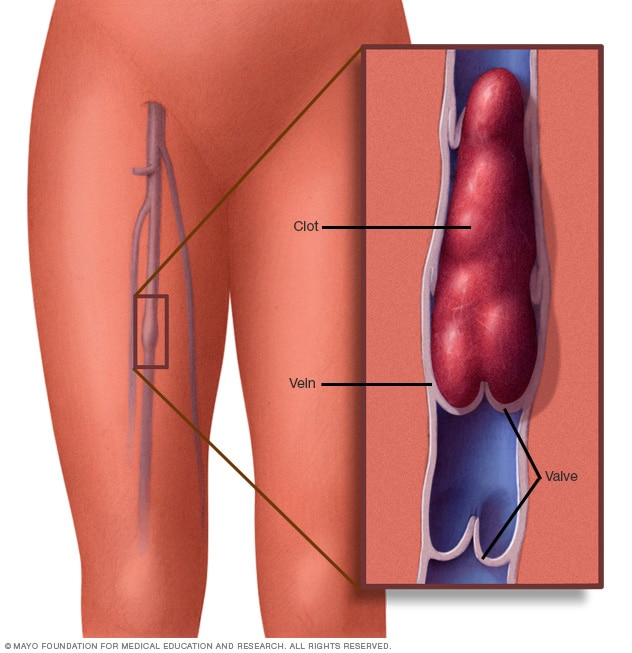
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs if a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in body, usually in legs. Deep vein thrombosis causes leg pain or swelling occur with cramps or no symptoms. Deep vein thrombosis develops if certain medical conditions affect blood clots. It happens if not mobile for long time after surgery confined to bed. Deep vein thrombosis is serious because blood clots in veins break loose, travel through bloodstream and lodge in the lungs blocking blood flow oxygen by pulmonary embolism. A lack of fresh oxygen from lungs causes breathing difficulties and shortage of breath so life threatening. Treatment is for 5-7 days or typically for 3-6 months, though blood thinners are continued for life if clotting disorder increases risk of another clot. After seven days, the clot is unlikely to be completely resolved so total time taken depends on the size of the clot. Most blood clots occur in lower legs and form when an individual is inactive for a lengthy period of time. A blood clot may develop in a patient’s leg after spending hours sitting or cramped on a plane. The symptoms experienced vary based on a size of clot, bigger clots are more painful than a smaller-sized ones. Those who have a blood clot in an arm or leg can experience swelling and tenderness. If the clot is small, minor calf swelling can occur but bigger blood clots cause whole leg or arm to swell. Those who have a clot notice a warm sensation or the affected area may turn bluish in color. The symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis signs and symptoms can include: Swelling in the affected leg. Rarely, there’s swelling in both legs.
- Pain in leg often starts in calf and feels like cramping soreness.
- Red or discolored skin on the leg.
- A feeling of warmth in affected leg.
Deep vein thrombosis occurs without noticeable symptoms sometimes. See a doctor if developed signs or symptoms of deep vein thrombosis, contact doctor. If developed the signs or symptoms of a pulmonary embolism a life-threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis seek medical attention. Pneumonia an inflammatory condition of lung affects small air sacs or alveoli. The breathing tube of lungs of clusters of tiny air sacs become inflamed and fill up with fluid. Symptoms includes some combination of dry cough, chest pains, fever and trouble breathing. Triggered by blood clot blocks wind pipes of lungs make it difficult to breath without oxygen tank or oxygenator. Pneumonia caused by infection with virus, bacteria or micro organisms, medication, conditions like autoimmune diseases. Risk factors are lung diseases, cystic fibrosis and COPD, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, inability to cough following stroke, weak immune system. Diagnosis of symptoms and physical examination, chest X-ray, blood tests and culture of sputum helps confirm a diagnosis. This diseases in hospitals, health care, causes associated pneumonia. Vaccine prevent pneumonia, handwashing, no smoking. Treatment depends on the underlying causes of pneumonia, bacteria is treated with antibiotics. Pneumonia, caused by bacteria white blood cell count is high, fall in severe cases. Viral mycoplasma pneumonia white cell count is low or normal severe pneumonia hospitalized. Oxygen therapy for low oxygen levels.
The warning signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort worsens when taking deep breath or cough
- Feeling lightheaded, dizzy, fainting
- Rapid pulse rates
- Coughing up blood
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Blood in urine
Blood in Urine and some causes gross hematuria, infection, trauma, kidney stones, cancer, blood cell disorders, medications, strenuous exercise. We do not know why strenuous exercise causes blood leaking in the urinary tract, but it could be fluid balance (dehydration), blood cell breakdown, liver or bladder trauma. Treatment is by medication, drinking plenty of water to avoid infections. People need in certain extreme cases the red blood clots removed surgically or medication, treatment by leaches work effectively. Blood thinning medication of aspirin or medical doctor prescribes medicines to treat patient. It must be treated urgently to stop lungs running out of air due to blocked clot as a red blood clot in lungs causes shortage of breath or no blood circulation means death. A respiratory circulatory system blood clot produces blood poisoning from the decomposing blood matter. The blood is exchanged using centrifugal transfusion to replace coagulated blood. If it’s done early saves lives but delays of waiting for machine worsen patient’s survival. A patient must seek help early so as not to self – sabotage essential treatment for life because life is in the blood. 
The widespread use of opioids to treat pain frequently prompts concerns about addiction and even deaths. So, why are these sometimes dangerous drugs still being given to patients? Much stronger than many of the other options, opioids are among the world’s most commonly prescribed painkillers. These drugs – including morphine, tramadol and fentanyl used to treat pain caused by everything from heart attacks to cancer has side effects. In the UK they were recently linked to the deaths of hundreds of elderly hospital patients, while the US is battling a well-documented opioid epidemic. Why not use other painkillers to avoid the risk of harm, addiction blood clots and breathing problems? These painkillers literally kill patients instead of alleviating excruciating pain. The triple harmful side-effects cause personality changes, confusion, hallucination so patients become less active. Instead of helping ease people’s pain at the moment harming them. With huge bonuses paid for use of such medications to pharmaceutical companies they are pushing it’s use more than safe non toxic options available.
A worldwide problem
Opioids work by combining with receptors in the brain to reduce the sensation of pain and they are highly effective. However, opioid receptors are present in areas of the brain responsible for breath control and high doses dangerously reduced rate of breathing as cause of almost all opioid deaths. Inquiry into Gosport said more than 450 people died between 1989 and 2000 from administration of “dangerous” amounts of opioids without medical justification. In US, increasingly widespread prescription of opioids to treat long-term pain led to epidemic addiction. In 2016, 11.5 million people in the US misused prescription opioids, and 42,249 died from overdoses. In England, GPs prescribed 23.8 million opioid-based painkillers in 2017 a rise of 10 million prescriptions since 2007. Since those with chronic pain require strong painkillers some are killed by overzealous use due to need to control excruciating pain and make patients comfortable. Those with sickle cell disease (SCD) have signs of the disease during the first year of life, around 5 months of age. Symptoms and complications of SCD are different for each person and can range from mild to severe pain. The reason infants don’t show symptoms at birth is because baby or fetal haemoglobin protects the red blood cells from sickling. When the infant is around 4 to 5 months of age, the baby or fetal haemoglobin is replaced by sickle hemoglobin and the cells begin to sickle. SCD is a disease that worsens over time. Treatments are available can prevent complications and lengthen lives of those who have this condition. The treatment options can be different for a person depending on symptom’s severity. Hydroxyurea (pronounced hye droks ee yoor EE a) is a medicine that can decrease several complications of SCD. This treatment is safe if given by medical specialists experienced in caring for patients with SCD. Side effects of taking hydroxyurea during pregnancy or for a long time are not completely known. The Food and Drug Administration approved a new medicine to reduce the number of sickle cell crises in adults and children older than age five; it is called L-glutamine. Another treatment, which can actually cure SCD, is a stem cell transplant (also called a bone marrow transplant); this procedure infuses healthy cells, called stem cells, into the body to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow (bone marrow is the center of the bone where blood cells are made). Although transplants of bone marrow or blood from healthy donors are increasingly used to successfully cure SCD, they require a matched donor (a person with similar, compatible bone marrow), and transplants sometimes cause severe side effects and occasional life-threatening illness or death. People with SCD and families should ask their doctors about benefits and risks of treatment options.
Sickle Cell Jaundice
Sickle cell jaundice bilirubin is released byproduct of red blood cells destroyed. The liver must process bilirubin to be excreted as bile into gut for digestion and passed out in the stools or urine. Jaundice occurs when there is too much bilirubin produced by too many red blood cells destroyed. The liver fails to process bilirubin in tummy so abdomen becomes swollen because of a build-up of fluid ascites. Liver and spleen may be enlarged plus unexcreted pile of dead red cells blocks passage of bile into gut. Jaundice disease is assessed and treated with significant symptoms of tiredness, ankle swelling, and also gastrointestinal bleeding, coma, confusion, ascites, etc. Clinical investigations show causes of jaundice increased bilirubin production increase of red blood cells destroyed. So haemolysis collection of blood in tissue red blood cell destroyed cause tiredness or lethargy called haemolyticanaemia. Failure of the liver to process bilirubin excretion diseases affects liver as viral infection, genetic diseases, excessive accumulation of chemicals (copper and iron. The disease Gilbert’s syndrome is a genetic disease causing jaundice by this method. Blockage of passage of bile into gut causes gallstones in bileduct of liver. Accumulation of gallstones requires the removal by surgery.
Jaundice Assessment
Complete jaundice assessment includes yellow eyes seen during clinical history, clinical examination, general or specific investigations. Review of clinical history and a complete routine medical history needs to be obtained. Medical history gives the causes of jaundice including pale stool, very dark urine, itchiness, gallbladder pain, tummy pain or others. A thorough general examination will be carried out specifically, liver and spleen should be felt for an enlargement. Other features include signs of anaemia lack of red blood cells in the body. A routine blood test checks of liver, blood system. The urine is tested to find exact cause in specific investigations by ultrasound for liver and tummy, CT of tummy, or direct visualisation of bile ducts in the tummy. A sample of liver tissue may be required for diagnosis in liver biopsy sometimes.
Treatment of Jaundiced Liver
Treatment of jaundice varies according to causes. A haematologist specialist in blood system, surgeon or physician is involved in treating causes of jaundice. Read more about liver and take care of yourself because the rate young people suffer from kidney disease is alarming. As a result some end up in Hospital on life support with kidney problems but can avert the menace of kidney disease.
TOP 6 CAUSES OF KIDNEY DISEASE:
1. Delay going to a toilet. Keeping your urine in your bladder for too long is a bad idea. A full bladder can cause bladder damage as urine in the bladder multiplies bacteria quickly. Once the urine refluxes back to the ureter and kidneys, the toxic substances can result in kidney infections, then urinary tract infections, nephritis, uremia and sepsis. When nature calls do it soon as you can.
2. Eating too much salt. You should eat no more than 5.8 grams of salt daily.
3. Eating too much meat. Too much protein in your diet is harmful for your kidneys. Protein digestion produces ammonia as a toxin very destructive to your kidneys. Too much meat than body needs equals more kidney damage.
4. Drinking too much caffeine. Caffeine is a component of many sodas and soft drinks. It raises your blood pressure and your kidneys start suffering. So you should cut down the amount of coke you drink daily.
5. Drinking water. Our kidneys should be hydrated properly to perform their functions well. If not drinking enough water the toxins can start accumulating in the blood, as there isn’t enough fluid to drain them through kidneys. Drink more than 10 glasses of water daily. An easy way to check if you are drinking enough water: look at the colour of your urine; the lighter the colour, the better.
6. Early treatment. Treat all your health problems quickly properly and have health checks regularly. Help yourself God will protect you and your family from every disease.
(3) Avoid Tablets as very dangerous:
* D-cold
* Vicks Action-500
* Actified
* Coldarin
* Cosome
* Nice
* Nimulid
* Cetrizet-D
They contain Phenyl Propanol-Amide PPA causes strokes so banned in USA.
* Doctors in United States have found new cancer in human beings, caused by Silver Nitro Oxide. Whenever you buy recharge cards, don’t scratch with your nails, as it contains Silver Nitro Oxide coating and can cause skin cancer.
Important Health Tips:
1. Answer phone calls with the left ear.
2. Don’t take medicine with cold water.
3. Don’t eat heavy meals after 5pm.
4. Drink more water in morning, less at night.
5. Best sleeping time is 10pm to 4 am.
6. Don’t lie down immediately taking medicine or after meals.
7. If phone’s battery is low to last bar do not answer phone because radiation is 1000 times stronger. Knowledge is power.
Signs or symptoms of acute liver failure include:
- Yellowing of skin and hands, feet
- Yellow eyeballs jaundiced
- Pain in upper right abdomen
- Abdominal swelling
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- General sense of feeling sick unwell malaise
- Disorientation or confusion
- Sleepiness
When to see a doctor
Acute liver failure can develop quickly in an otherwise healthy person and life-threatening. If one suddenly developed yellowing of eyes or skin; tenderness in upper abdomen or unusual changes in mental state, personality or behaviour seek medical attention right away.
Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation
Pluripotential cells in bone marrow differentiate into red blood cells, white cells and platelets. The Immune system impacts red and white cells. And recent advances help understand coagulation in the heterogeneous group of diseases, thrombotic microangiopathies (TMA) characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anaemia thrombocytopenia platelet clumping in microcirculation ischemic organ dysfunction neurologic symptoms. Increased thrombosis was reported in different hemolytic anaemia (HA), particularly in sickle cell disease (SCD), and thalassemia. The different patho-physiologies, hemolysis have the procoagulant condition. The mechanism involves abnormal red blood cell (RBC) properties. And the increased plasma concentrations of microparticles and a release of cell-free haemoglobin RBC arginase result in impaired nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, increased blood concentration of oxidants, endothelial dysfunction. Major clinical consequence increase developing venous thrombosis, clinical sequelae of hemolysis symptom by NO depletion increased cell free plasma haemoglobin. Hemoglobinemia feature of the HA possibly contributing factor to explain clinical manifestation’s thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs) characterized by microangiopathic HA and thrombocytopenia. The condition characterising intravascular hemolysis specific symptoms seen cell-free plasma haemoglobin sequalae. Conditions such as SCD and thalassemia syndromes and hemolytic conditions with substantial intravascular hemolysis. SCD, and the thalassemia represent common genetic disorders worldwide. Though different patho-physiologies, patients with both diseases share clinical manifestations, including thrombotic complications. So stroke in patients caused by large-vessel obstruction superimposed thrombosis, is one of the major complications in SCD. Pulmonary hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening complication in SCD, as documented by echo-cardiography (pulmonary artery pressure [PAP] > 30%) in approximately 30% adult patients with SCD screened. Autopsy showed evidence of new and old thrombi in pulmonary vasculature in up to 75% of SCD patients at the time of death. A recent report based on data by National Hospital Discharge Survey in U.S. shows patients with SCD younger than 40 years old had higher discharge diagnosis of pulmonary embolism than African Americans without SCD (0.44% vs 0.12% the prevalence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) was similar. National In-patient Sample from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project of Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, from 2000 to 2001, reported SCD is a significant risk factor for pregnancy-related venous thrombo embolism, with an odds ratio of 6.7 (95% confidence interval: 4.4–10.1. The thrombophilic status in SCD has been well documented as multifactorial, involving hemostatic changes, activation of the coagulation cascade and endothelial activation as shown by elevated levels of endothelial adhesion proteins (ICAM-1. ELAM-1,VCAM-1, von Willebrand factor [VWF] and thrombomodulin). Intimal hyperplasia was found in a variety of vascular beds, including pulmonary, renal, splenic, and placental vessels, and in arterioles adjacent to leg ulcers of patients with SCD. Most SCD-related complications said to be caused by the microvascular occlusion and ischemic tissue necrosis following adhesion of erythrocytes (RBCs) and other cellular elements to vascular endothelium. So clinical series describe occurrence of DVT, pulmonary embolism and portal vein thrombosis in patients with β-thalassemia major and β-thalassemia intermedia. In a recent survey of 8860 patients with β-thalassemia in the Mediterranean region and Iran, the overall prevalence of various thrombotic events was 1.65%, precisely 0.9% in thalassemia major and 4.0% in thalassemia intermedia. Was common in SCD, stroke was reported in patients with β-thalassemia major from Greece and Italy an incidence of 20% and 2%, patients with β-thalassemia hemoglobin E (HbE) disease. Complication occurs commonly in the patients not regularly transfused. Evidence of asymptomatic brain damage reported by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with β-thalassemia intermedia and is inversely correlated with Hb level and increasing age. PAH is increasingly recognized as part of the clinical spectrum for adult β-thalassemia patients, with a frequency ranging from 10% to 74%; the overall higher rate in thalassemia intermedia. Regular transfusions thought to reduce the risk of thrombosis in thalassemia. In recent study, Singer et al found PAH in transfused patients with thalassemia major, most of whom splenectomized, suggesting regular transfusion does not prevent PAH, thrombotic complications. Several factors implicated pathogenesis of the hypercoagulable state, specific changes in lipid membrane composition of abnormal RBCs increased expression negatively charge phosphatidylserine outer surface. Postsplenectomy thrombocytosis, cardiac dysfunction, liver dysfunction lead to protein C and protein S reduction. Suggest inefficient spleen, hematologic hemolytic diseases contribute to an increased propensity to thromboembolic complications. Both β-thalassemia or sickle cell anemia, have a high proportion of patients without splenic function due to surgical splenectomy or due to functional hyposplenism. In a series of 83 patients with β-thalassemia intermedia followed for 10 years, 29% developed pulmonary embolism, DVT of lower extremities and portal vein thrombosis. Development of complications attributed to presence of high platelet counts after splenectomy. Moderate thrombocytosis in the older children, adults with SCA a consequent loss of splenic sequestration autosplenectomy in patients. Literature on relationship between splenectomy or autosplenectomy and thrombosis in SCA is scant. Specific features of thrombotic complications in patients with SCD and thalassemia share similar pathogenesis. Intravascular hemolysis is a common feature of both SCD and thalassemia. Recent evidence associates chronic intravascular hemolysis with a state of endothelial disfunction.
Red Blood Cells
The major stimulus to red blood cell (RBC) production erythropoetin, which is produced in the kidney. Anaemia is decrease in number or concentration of red blood cells amount of concentration of haemoglobin as a common inducer of erythropoetin production. It is not the number or concentration of RBCs that stimulates erythropoetin production, but decreased oxygenation of the blood. The number of red blood cells increase in chronic hypoxia as occurs in those who live at high altitudes. Effectiveness of the red blood cell in carrying oxygen depends on oxygen supply, number of red blood cells and health of red cells:
1) In aplastic anemia, the marrow as a whole is suppressed, by radiation or drugs. Red cells and other blood cells decrease in number (pancytopenia) in aplastic anemia.
2) Anaemia develops from significant blood loss.
3) If iron, an important ingredient of the haemoglobin molecule is deficient in the diet, the patient develops an iron deficiency anaemia. Iron is transported in blood by plasma protein transferrin, stored intracellularly on the protein, ferritin. Deficiency of transferrin results in an iron deficiency anaemia.
4) Vitamin Bu and folic acid important in synthesis of DNA, in development of RBCs from their precursor cells in the marrow. A deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid leads to megaloblastic anaemia in which the RBCs are large, fragile and short-lived. Intrinsic factor, produced by parietal cells in the gastric mucosa, normally combines with vitamin B12, protecting it from gastric digestion, and facilitates its transport across intestinal mucosal membrane. Lack of intrinsic factor, results in a megaloblastic anaemia (pernicious anaemia by failure of B12 absorption.
5) Defects in structure of haemoglobin may be responsible for the anemia. In sickle cell anemia, a recessive gene results in abnormal haemoglobin, which distorts the red cells into a sickle shape in states of low oxygenation. The RBC becomes very fragile, is short-lived, and can clog blood vessels. About 8% of the black population carries the gene. Individuals with the heterozygous state typically are normal, although sickling can occur in marked states of hypoxia. True sickle cell anemia, the homozygous state, occurs in about 0.3% of blacks.
Read more about treatment guidelines »
Hand-Foot Syndrome
Swelling in the hands and feet usually is the first symptom of SCD. This swelling, often along with a fever, is caused by the sickle cells getting stuck in the blood vessels and blocking the flow of blood in and out of the hands and feet. One is at a higher risk of developing blood clots when blood pools in the lower extremities. Elevating the feet and legs will allow veins to return blood to the heart more efficiently and thus reduce the chances of clotting. Those who expect to be bedridden for a long time, such as after surgery or an illness, should put blocks under the foot of a bed to elevate the legs, keeping them slightly higher than heart. Alternatively, placing pillows under one’s lower half will give the same result.
Treatment
The most common treatments for swelling in hands and the feet are pain medicine and an increase in fluids, such as water. Those going on long flight planning for surgery, or other actions that put them at risk for blood clotting, drinking plenty of water can reduce the chance of developing subsequent clots. Proper hydration prevents blood clots in a variety of ways; it increases fluid in blood vessels, diluting the ratio of blood cells and reducing viscosity, lowering risk of clotting. Additional liquid washes away irritants in bloodstream damaging endothelium and blood cells. Blood clot is natural response to damage, washing away toxins significantly lowers risk. Choose water over juices and sodas high sugar liquids leads to dehydration.
Do You Use the Emergency Department for Care of SCD?
Pain “Episode” or “Crisis”
Pain is the most common complication of SCD, and the number 1 reason that people with SCD go to the emergency room or hospital. When sickle cells travel through small blood vessels, they can get stuck and clog the blood flow. This causes pain that can start suddenly, be mild to severe, and can last for any length of time.
Prevention
There are simple steps that people with SCD can take to help prevent and reduce the number of pain crises, including the following:
- Drink plenty of water.
- Try not to get too hot or too cold.
- Try to avoid places or situations that cause exposure to high altitudes (for example, flying, mountain climbing, or cities with a high altitude).
- Try to avoid places or situations with exposure to low oxygen levels (for example, mountain climbing or exercising extremely hard, such as in military boot camp or when training for an athletic competition).
- Adults with severe SCD can take a medicine called hydroxyurea to help reduce the number of pain crises. People taking hydroxyurea are checked often by a doctor to prevent complications, including an increased risk of infections.
- Research shows that babies and children with SCD can also benefit from hydroxyurea therapy.
Treatment
Most pain related to SCD can be treated with over the counter pain medications such as ibuprofen and aspirin. Some people who have severe pain are given opioid (i.e. morphine) medications daily, with additional pain medication. Some people may be admitted to the hospital for intense treatment.
Fast Fact
Taking iron supplements will not help people with sickle cell disease. This type of anemia is not caused by too little iron in the blood; it’s caused by not having enough red blood cells. In fact, taking iron supplements could harm a person with sickle cell disease because the extra iron builds up in the body and can cause damage to the organs.
Anaemia
Anaemia is very common complication of SCD. With SCD, the red blood cells die early. This means there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout body. When this happens, a person might have:
- Tiredness
- Irritability
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- A fast heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Pale skin color
- Jaundice (yellow color to the skin and whites of the eyes)
- Slow growth
- Delayed puberty
Treatment
Blood transfusions are used to treat severe anemia. A sudden worsening of anemia resulting from infection or enlargement of the spleen is a common reason for a transfusion. Multiple blood transfusions, however, might cause health problems because of the iron content of blood. Iron overload, called hemosiderosis, can damage liver, heart, pancreas and other organs, leading to diseases such as diabetes mellitus. Iron chelation therapy should be started in patients with SCD receiving regular blood transfusions to reduce excess iron levels. Above all, check and ensure the blood donor does not suffer from blood clots as sometimes it affects recipients of such blood.
Infection
People with SCD, especially infants and children, are more at risk for infections, especially those due to bacteria with capsules because of damage to the spleen. Pneumonia is a leading cause of death in infants and young children with SCD.
Prevention
Vaccines can protect against harmful infections.
- Washing your hands is one of the best ways to help prevent getting an infection. People with SCD, their family, and other caretakers should wash their hands with soap and clean water many times each day.
- Because bacteria in some foods can be especially harmful to children with SCD, food should be prepared safely.
- Vaccines can protect against harmful infections. Children with SCD should get all regular childhood vaccines, plus a few extra. Adults should have the flu vaccine every year, as well as the pneumococcal vaccine and any others recommended by a doctor.
- Take penicillin (or other antibiotic prescribed by a doctor) every day until at least 5 years of age.
See a tip sheet on how to help prevent infection »
Treatment
Infections are treated with antibiotic medicines and sometimes blood transfusions. At the first sign of an infection, such as a fever, it is important to see a doctor right away as this may represent a medical emergency for people with SCD. Early treatment of infection can help prevent problems.
Acute Chest Syndrome
This can be life-threatening and should be treated in a hospital. Symptoms and signs are similar to pneumonia. Signs and symptoms include chest pain, coughing, difficulty breathing, and fever. Blood clot travels to lungs doctors call pulmonary embolism. Clots reach lungs if small is non-life threatening but smaller clots causes substantial damage to lungs. If clot is large, can stifle proper blood flow and become deadly, so quick treatment is essential. So most common symptom to look for is sudden shortness of breath; if individual is short of breath or lacks physical movement is suffering from pulmonary embolism. A condition causes patient to experience chest pain, breathing problems, heart palpitations. In some cases, a pulmonary embolism causes one to cough up blood as well.
Prevention
Adults with severe SCD can take a medicine called hydroxyurea to help prevent acute chest syndrome. People taking hydroxyurea monitored closely with regular blood testing and dose adjustments to prevent complications. A person on bed rest or recent surgery can use an incentive spirometer, also called “blow bottle,” to help prevent acute chest syndrome.
Treatment
Depending on cause, treatment might include oxygen, medicine to treat an infection, medicine to open up airways to improve air, and blood transfusions. Cut down on salts and fatty cholesterol because salt irritates endothelium or inner lining of veins and arteries. The blood vessels do not work efficiently in moving blood around body. This leads to blood pooling in lower extremities, where it is more likely to clot. Damage to endothelium makes blood cells more to stick to walls of vessels, increasing the risk of clots. Excessive salt intake is harmful to the cardiovascular system in a variety of ways, with blood clots one of the more significant risks. Decreasing salt intake, cutting out all canned and processed foods significantly reduces the risk of blood clots.
Splenic Sequestration
This can be life-threatening and should be treated in a hospital. It happens when a large number of sickle cells get trapped in the spleen and cause it to suddenly get large. Symptoms include sudden weakness, pale lips, fast breathing, extreme thirst, abdominal (belly) pain on the left side of body, and fast heartbeat.
Parents of a child with SCD should learn how to feel and measure the size of their child’s spleen and seek help if the spleen is enlarged.
Prevention
For those who have had a very severe, life-threatening episode of splenic sequestration or who have had many episodes in the past, it might be necessary to have regular blood transfusions or the spleen can be removed (called splenectomy) to stop it from happening again.
Treatment
Treatment typically is a blood transfusion. This should be done in consultation with a blood specialist as patients sometimes become overloaded with fluid when the blood is released from the spleen. Removal of blood may be necessary to prevent this happening.
Vision Loss
Vision loss, including blindness, can occur when blood vessels in the eye become blocked with sickle cells and the retina (the thin layer of tissue inside the back of the eye) gets damaged. Some patients develop extra blood vessels in the eye from the lack of oxygen.
Prevention
People with sickle cell disease should have their eyes checked every year to look for damage to retina. If possible, this should be done by an eye doctor who specializes in diseases of the retina.
Treatment
If the retina is damaged by excessive blood vessel growth, laser treatment often can prevent further vision loss.
Leg Ulcers
This usually occurs on the lower part of the leg. They happen more often in males than in females and usually appear from 10 through 50 years of age. A combination of factors cause ulcer formation, including trauma, infection, inflammation, and interruption of the circulation in the smallest blood vessels of the leg.
Treatment
Leg ulcers can be treated with medicated creams and ointments. Leg ulcers can be painful, and patients can be given strong pain medicine. Management of leg ulcers could also include the use of cultured skin grafts. Treatment is provided in specialized centers. Bed rest and keeping leg or legs raised to reduce swelling helpful though not always possible.
Stroke
A stroke can happen if sickle cells get stuck in a blood vessel and clog blood flow to the brain. About 10% of children with SCD will have a symptomatic stroke. Stroke can cause learning problems and lifelong disabilities.
Prevention
Children who are at risk for stroke can be identified using a special type of exam called, transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD). If the child is found to have an abnormal TCD, a doctor might recommend frequent blood transfusions to help prevent a stroke. People who have frequent blood transfusions must be watched closely because there are serious side effects. For example, too much iron can build up in the body, causing life-threatening damage to the organs.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Sickling of red cells can increase blood coagulation and induce an increased risk of blood clot in a deep vein (DVT), or in the lung (PE) if the blood clot moves from the deep veins. People with SCD have a high chance of developing DVT or PE. DVT and PE can cause serious illness, disability and, in some cases, death.
Prevention and Treatment
Medication is used to prevent and treat DVT and PE. PE requires immediate medical attention. For more information on DVT and PE visit https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/index.html.
Other Possible Complications
- Damage to body organs (like the liver, heart, or kidneys), tissues, or bones because not enough blood is flowing to the affected area(s).
- Malnutrition and growth retardation among adolescents can cause a delayed onset of puberty and, in males, infertility.
- Gallstones.
- Painful erection of the penis, called priapism, can last less than 2 hours or more than 4 hours. If it lasts more than 4 hours, the person should get urgent medical help. It can lead to impotence.
- A very rare form of kidney cancer (renal medullary carcinoma) has been associated with sickle cell trait.
Links to Other Websites
Sickle Cell Disease Association of America
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute Clinical Trials
Be The Match – Bone Marrow Transplantation
Reblogged as previously published